There is a lot of noise in the technology world, and this noise can make things confusing. It’s especially true for the non-geeks, who would prefer to focus on their business and just take advantage of technology to move their work forward.
You’ve likely heard such terms as “BPM,” “workflow automation,” and so on, whether it was on the Internet at large or here on the Pyrus blog.
We understand that these concepts can be confusing. That’s why we want to help you understand these terms more clearly today, so that you’ll be be better positioned to use the tools available to you to easily achieve your business goals, improve your team’s operational efficiency, and ultimately grow your business.
What is BPM?
BPM is an acronym for “business process management.” Different experts have defined business process management in different ways, so there’s really no industry-approved definition. Here, we will try to define it in the easiest way you can understand.
Business process management is the practice of reengineering and optimizing an organization’s business processes for improved performance, increased efficiency, and effectiveness.
To make it a bit clearer, let’s break it down to see what “business process” means.
What is a business process?
A business process is a set of related tasks, performed to accomplish a specific organizational goal. It can also be defined as a series of logically structured activities that produce a specific service or product for customers.
A perfect example is when a purchase order is created, approved, and issued to a vendor. The vendor supplies the goods or provides the services as needed and then sends an invoice. The accounts payable department receives the invoice, then processes and pays it after a series of approvals.
Business processes can be complicated, as they usually consists of different participants doing different things at different stages. But there’s a simpler concept out there: workflow.
Don’t confuse business process with workflow.
Business process is not workflow. Workflow is more straightforward than business process.
Think of BPM as an umbrella term, on which workflow is only one component. Workflow is more about taking a single piece of work from initiation to completion.
While a business process encompasses numerous related activities that cut across various departments and involving multiple workflows, participants, and stages, workflow deals with how individual processes are coordinated. That is, which tasks, information, or documents are passed from one participant to another for action, following a set of procedural rules.
BPM is not project management.
Some people make the mistake of thinking that BPM is the same as task management or project management. But that is not correct: BPM is neither task management nor project management, but it can still take place within the context of a project.
Project management is about planning and piloting a unique, transient endeavor (usually initiated to achieve planned objectives) from start to finish. Task management is about organizing and administering or supervising the conduct, performance, or execution of an activity arising out of a project.
Tasks and projects are often one-time and non-repetitive. Business process management is focused more on repeatable, ongoing processes following a set pattern.
For project and task management, you can use simple applications like Trello and Asana, but business process management requires more sophisticated software or a process-specific tool like Pyrus.
Why should an organization implement business process management?
Turns out organizations often implement business process management for a variety of reasons.
- Higher efficiency and productivity: Business process management facilitates the automation of repeatable workflows. This removes bottlenecks, eliminates redundant steps, and increases productivity.
- Improved agility: Business process management empowers an organization to play favorably in a competitive market. You can quickly adapt to changes, make progress, and stay ahead through the implementation of BPM.
- Reduced costs: With processes streamlined, your organization can save on the costs of operation.
- Better bottom line: BPM makes it possible for employees to spend more time on other productive activities. This translates into an improved bottom line, higher revenues, and reduced waste.
- Better visibility: BPM lets you monitor and control processes as you want. This only ever results in better visibility, making it possible to identify and remove bottlenecks.
- Happier workforce: With automated tasks, simplified processes, and easier access to information, employees are happier now to complete the tasks they dreaded before.
- Reduced fraud: Business process management enhances the design, execution, and monitoring of more conspicuous processes. This reduces the risk of fraud.
A Typical BPM Life-Cycle
A typical business process management follows the life-cycle given below to complete a business process:
- Designing
- Modeling
- Execution
- Automation
- Monitoring
- Control
- Measurement
- Optimization
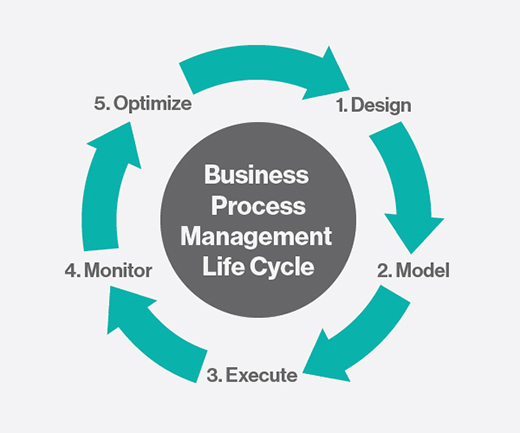
Here’s how it works in steps:
- Step #1: You design the process and determine how it should look.
- Step #2: You model it using business process management software.
- Step #3: You execute it by putting it in a business process management tool. (For efficiency, this step often involves automating the the workflows of the process using workflow automation software.)
- Step #4: You monitor and control the process (while in execution), driving compliance and redefining rules as necessary.
- Step #5: You measure and optimize. (This is where you gather data about how the system functions, and using the data to make improvements. Here’s a post we did on the most important accounts payable metrics to track.)
Some things to keep in mind:
- Tracking metrics is important for quantitatively determining how well the system is working in terms of accomplishing your planned objectives.
- Business process management is not one-off; it is an ongoing activity.
- Business process management needs time to get better. This is where optimization comes in. Optimization should be based on metrics and should support the objectives.
- Business process management is a practice; a discipline. It is something you do; not a product or something you own.
- The ultimate aim of business process management is to improve your business processes.
- Automation is a key feature of business process management, but it is not every business process or workflow that needs automation.
Business Process Automation (BPA)
Business process automation is the use of technology to cut costs and streamline business processes. It’s a technology-enabled, systemized method that simplifies complex, redundant business processes.
BPA focuses on replacing manual processes with automated ones so you can get more done in less time with less effort. It saves costs by reducing the need for human input and by preventing errors that would require extra time and resources to solve.
How to use business process management to your advantage
Business processes are characteristically slow, inefficient, and redundant. You need a system to optimize such processes. BPM does this for you by evaluating your processes and identifying areas that can be improved for better performance.
Here are some steps you can take to use BPM to your business’s advantage:
- Start by evaluating your current processes to see where you need to improve. Doing this will give you an idea of the key deficiencies in your current workflows, a foundation of knowledge that is necessary for streamlining your processes effectively. With this, you’d be able to make better decisions instead of operating on assumptions.
- Identify your goals. Do you want to increase the daily volume of a particular activity, for example? Identifying your goals will make it easy to make improvements more quickly. You’d also have a mental picture of where you are going with your BPM.
- Get the right people involved. You can’t really implement BPM by yourself, as it is an organization-wide endeavor. You need to carry your colleagues along with you. You need experts who can make meaningful contributions and steer the strategy to a successful end.
- Choose your workflow management system intelligently. The tools you use in implementing BPM can determine how successful it will turn out. Do your homework and pick just the best tool for your organization. You can check out our post on essential things to consider in choosing workflow automation software here.

Business process management is a complex topic. Regardless, it’s vital that you at least have an understanding of its basic components to be in an advantaged position where you are able to compete favorably in today’s technologically-driven business world.
This guide should be able to put you in that position of advantage. However, it’s also important that you not only know these things but actually implement them to see results.
Pyrus can help you get started in your BPM journey today. We specialize in turning complex, repetitive processes into simple and fun tasks through effective automation. Trusted by thousands of users around the world, Pyrus boasts of a business process management tool that your team will actually love to use. And you won’t have to pay for it. Sign up through the form below to get started.